DiffVax: Optimization-Free Image Immunization Against Diffusion-Based Editing
ICLR 2026
ICLR 2026
Current image immunization defense techniques against diffusion-based editing embed imperceptible noise into target images to disrupt editing models. However, these methods face scalability challenges, as they require time-consuming optimization for each image separately, taking hours for small batches. To address these challenges, we introduce DiffVax, a scalable, lightweight, and optimization-free framework for image immunization, specifically designed to prevent diffusion-based editing. Our approach enables effective generalization to unseen content, reducing computational costs and cutting immunization time from days to milliseconds, achieving a speedup of 250,000×. This is achieved through a loss term that ensures the failure of editing attempts and the imperceptibility of the perturbations. Extensive qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that our model is scalable, optimization-free, adaptable to various diffusion-based editing tools, robust against counter-attacks, and, for the first time, effectively protects video content from editing.
|
(a) An attacker performs malicious editing on an original image. (b) Existing defenses immunize images by solving a costly optimization problem for each image individually, taking over 10 minutes per image. (c) DiffVax enables scalable protection by first training an immunizer model (green box) on a diverse dataset. Once trained, the model can immunize unseen images with a single forward pass, producing effective perturbations in approximately 70 milliseconds per image. |
|
Our process begins with the immunizer model $f(\cdot;\theta)$ which generates imperceptible noise $\epsilon_{im}$ to be applied to original image $I$. This noise is applied to the masked region $M$ of the image, resulting in immunized image $I_{im}$. The immunized image is then processed by a diffusion-based editing model $SD(\cdot)$ using a text prompt $P$ and the complementary mask $\sim M$ to edit the background of the original image. The training aims to minimize two loss terms $\mathcal{L}_{noise}$ and $\mathcal{L}_{edit}$, which penalizes the applied noise magnitude, and if the edit is successful, respectively. During training, the immunizer learns to generalize across diverse images, ensuring editing attempts fail while preserving visual fidelity. This end-to-end framework enables robust, scalable immunization against diffusion-based editing for both images and videos. |
Prompt
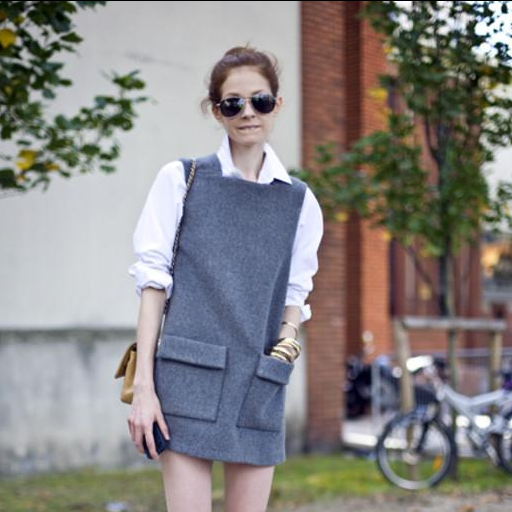
Original Image
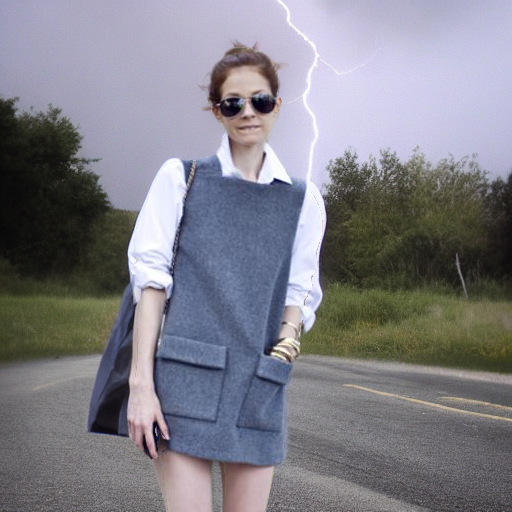
Edited Image
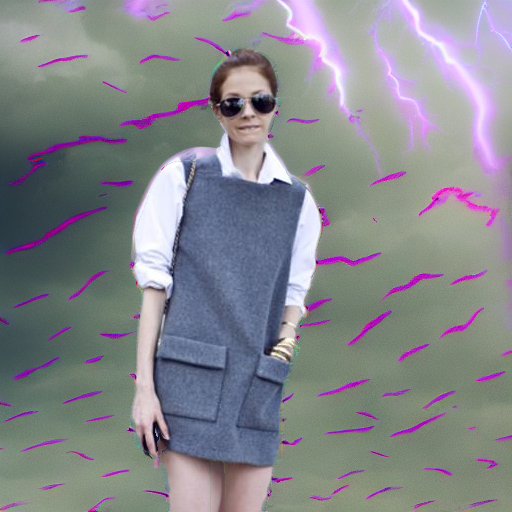
Edited Immunized Image
"in a prison"
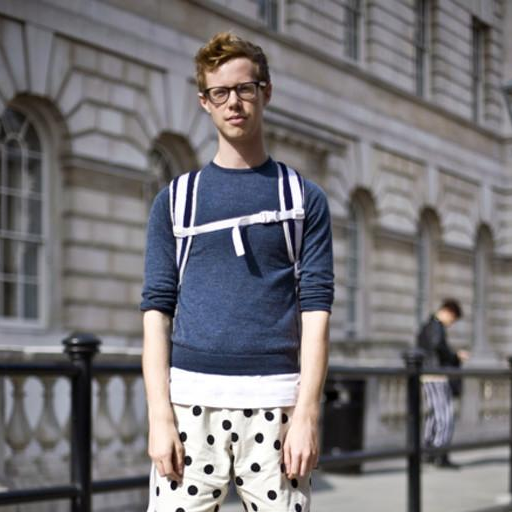
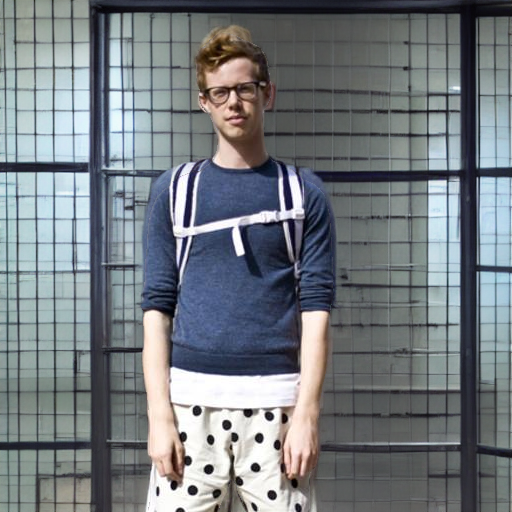
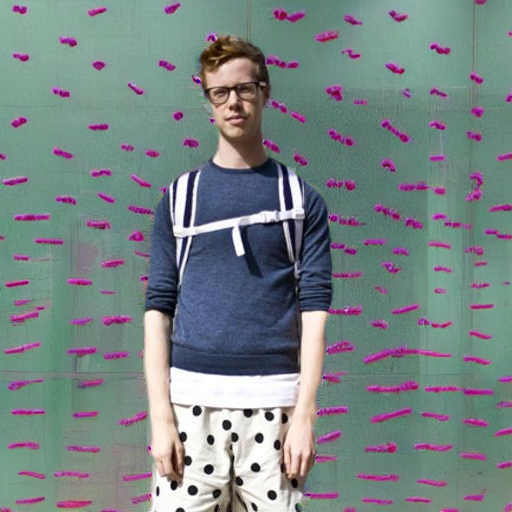



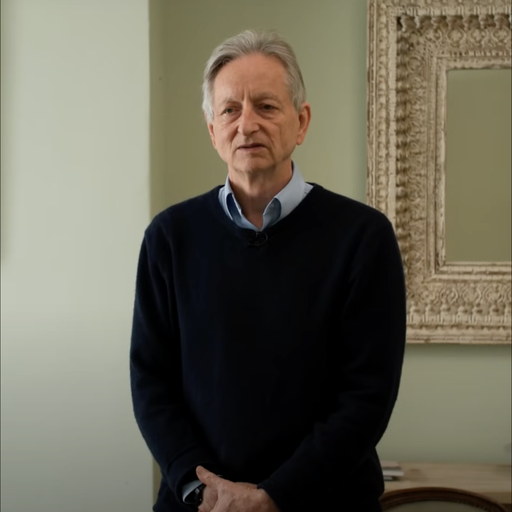
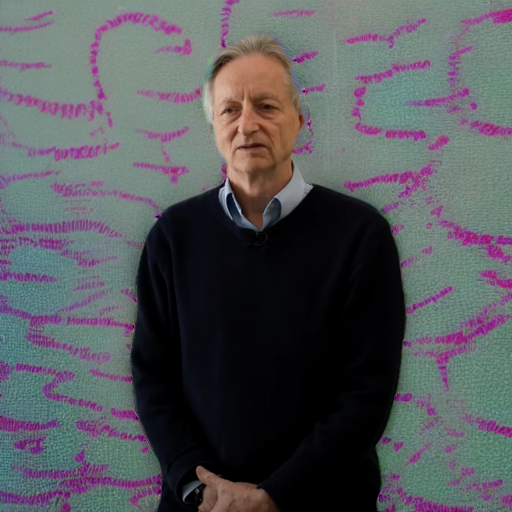
"Geoffrey Hinton at a political protest"
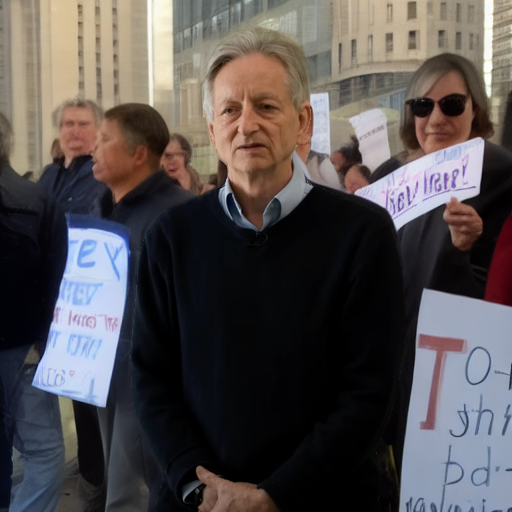



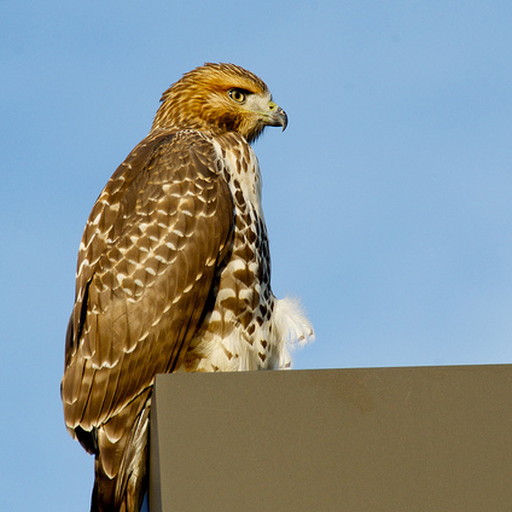
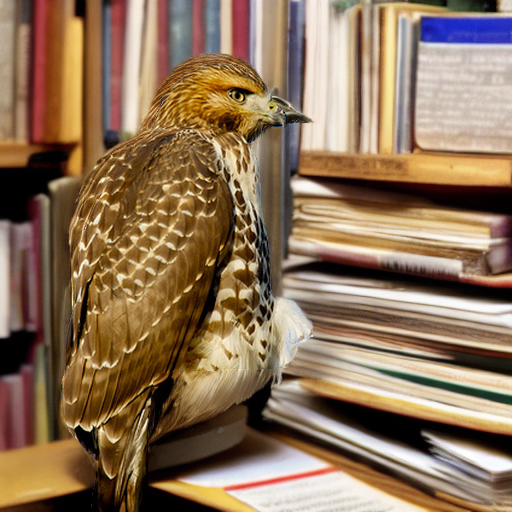
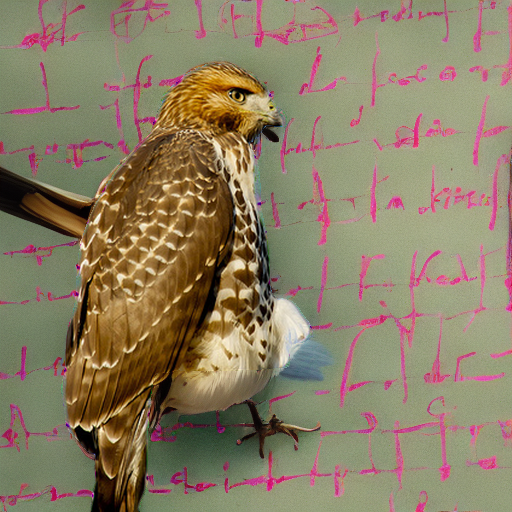
"an eagle sitting on a table in a library"



"add sunglasses"
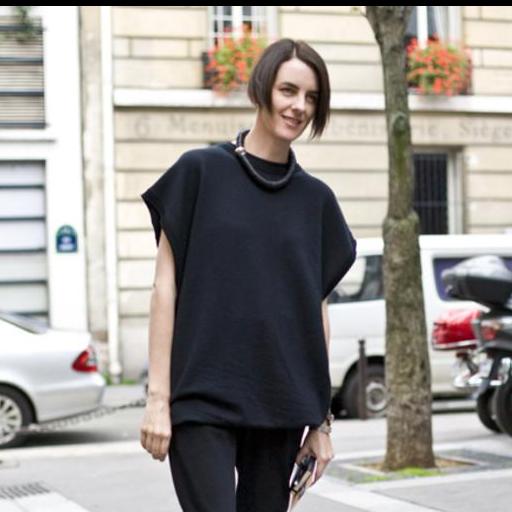
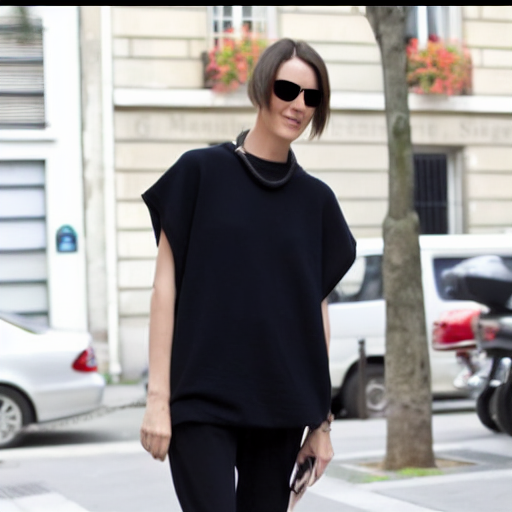
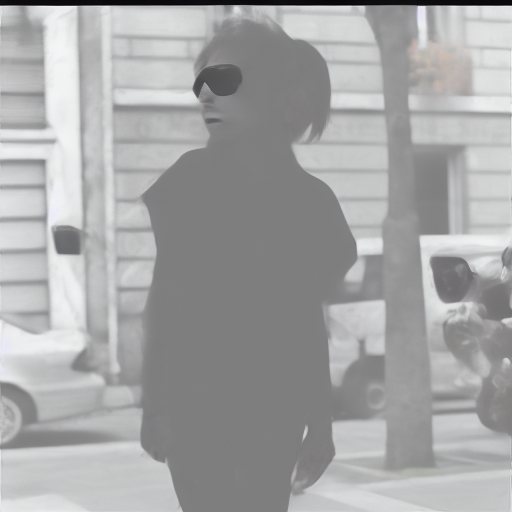



"standing in an abandoned carnival"
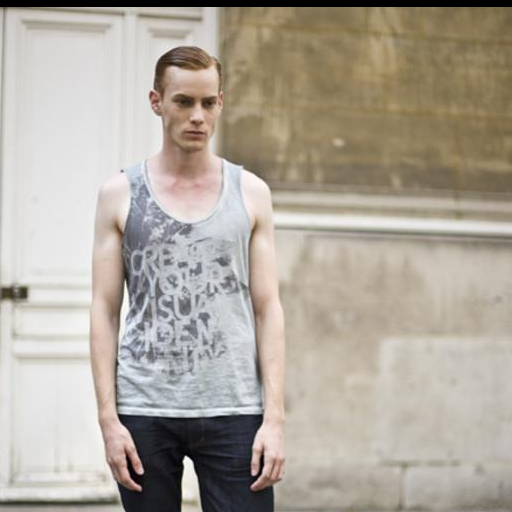
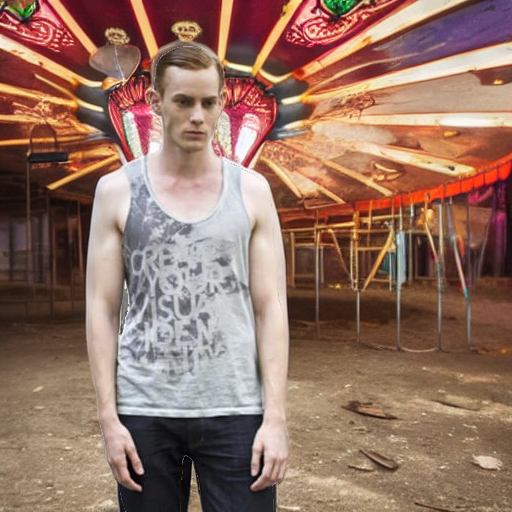
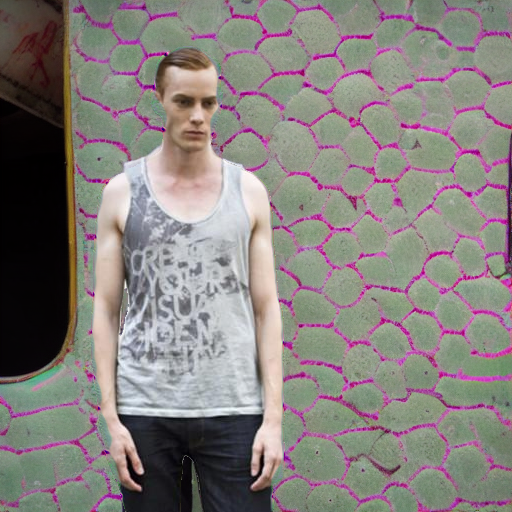



"watching a theater performance"
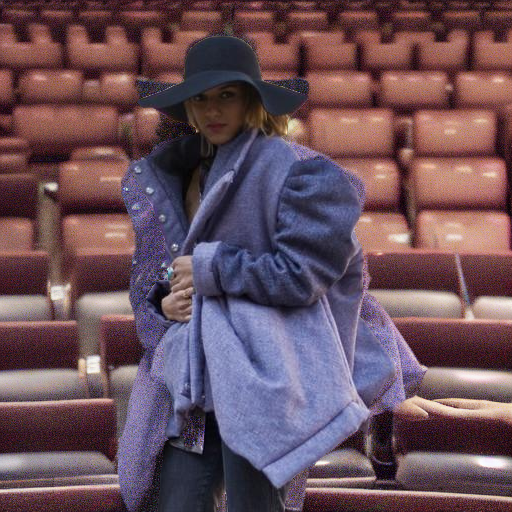
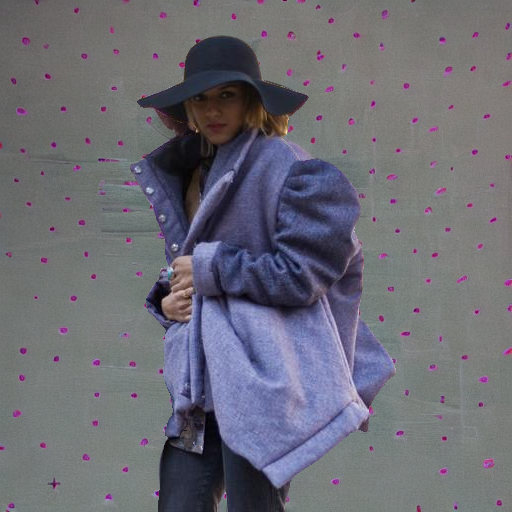



"in front of a hotdog stand"
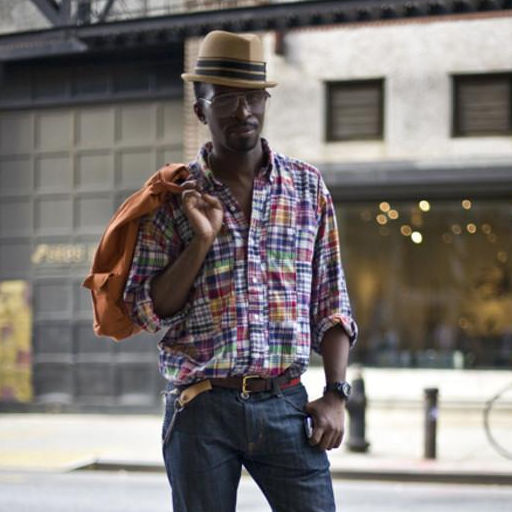
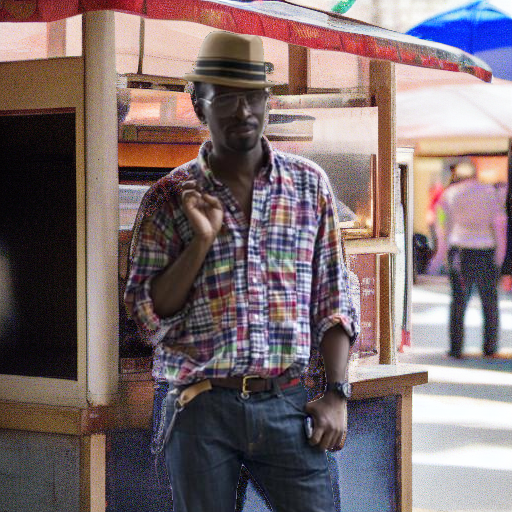
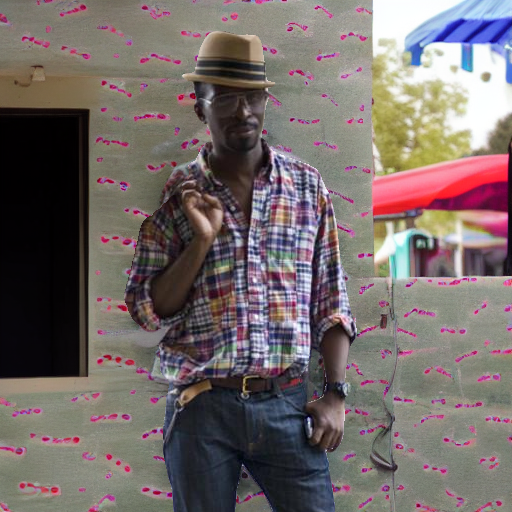



"under a turbulent sky with lightning"



"in a garage"
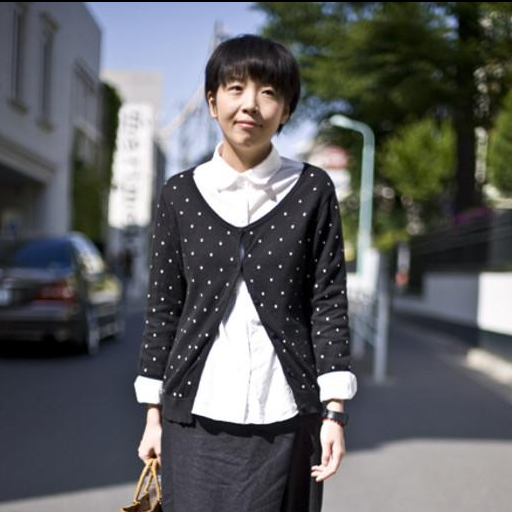
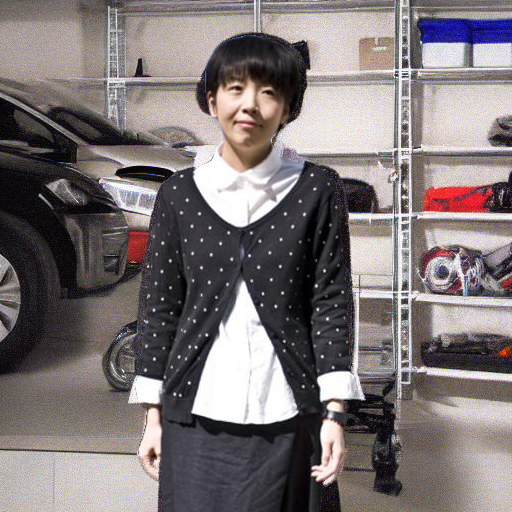
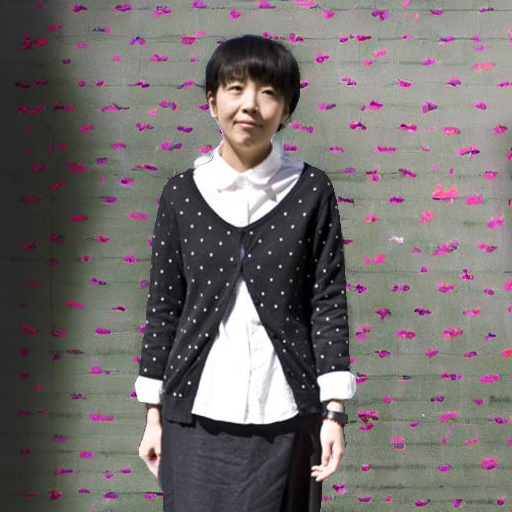



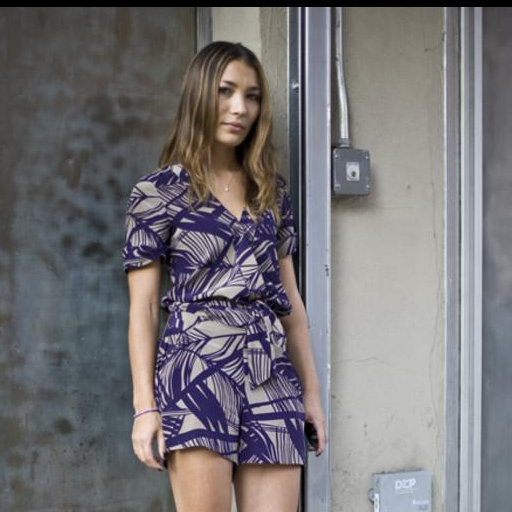
"in a church with wooden pews"
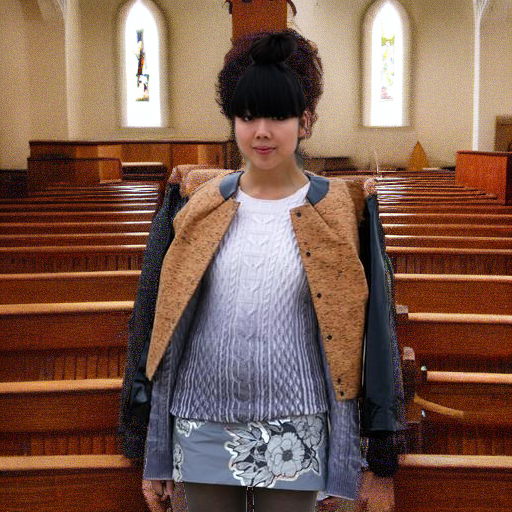
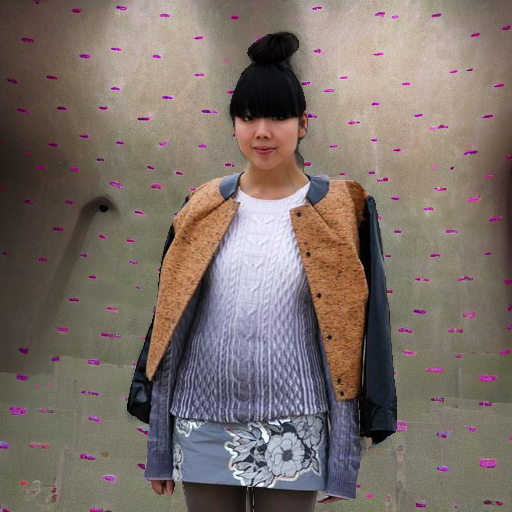



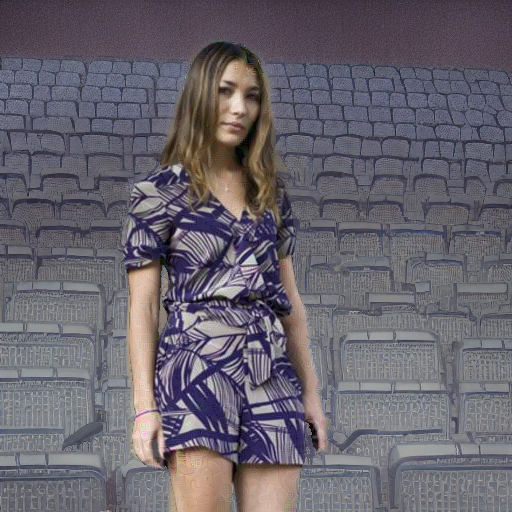
Original Video
Edited Video
Immunized Edited Video
"in snowstorm"
Original Image
Edited PhotoGuard-D
Edited Attacked PhotoGuard-D
Edited DiffVax (Ours)
Edited Attacked DiffVax
Denoiser Attack
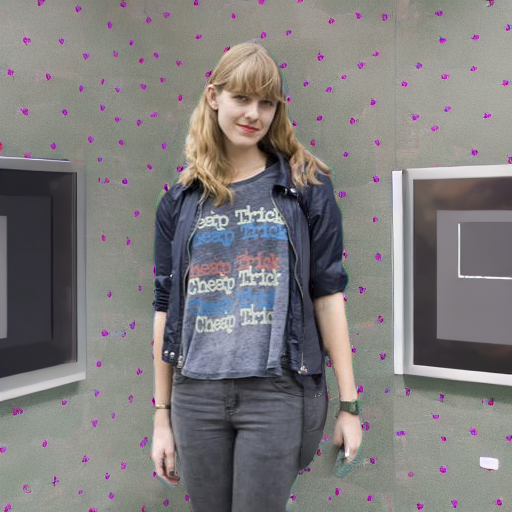
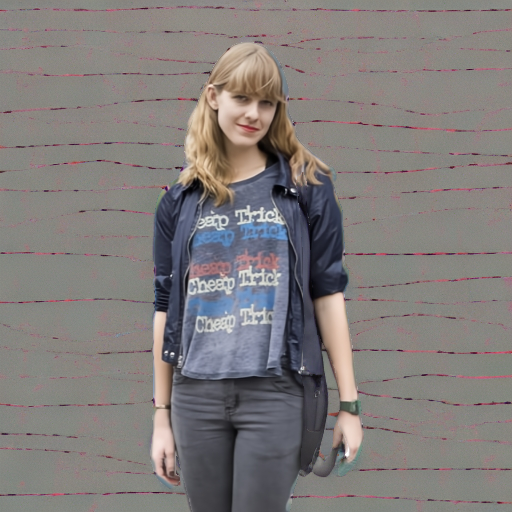
Prompt: "a person in a cinema"
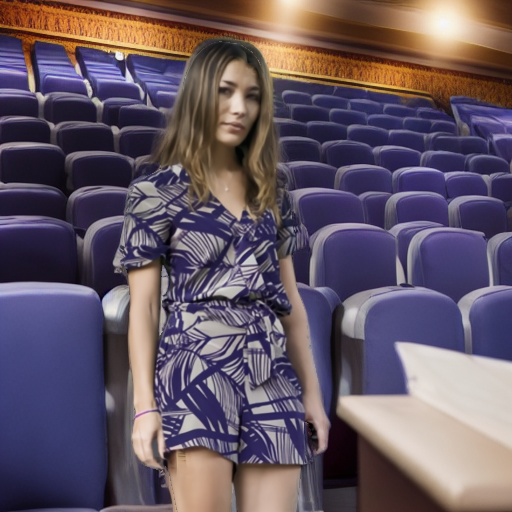
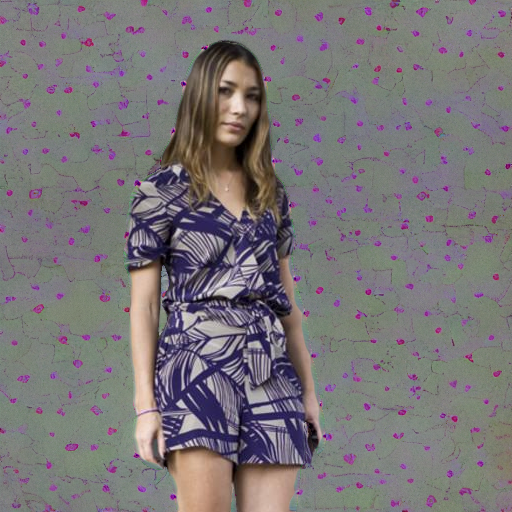
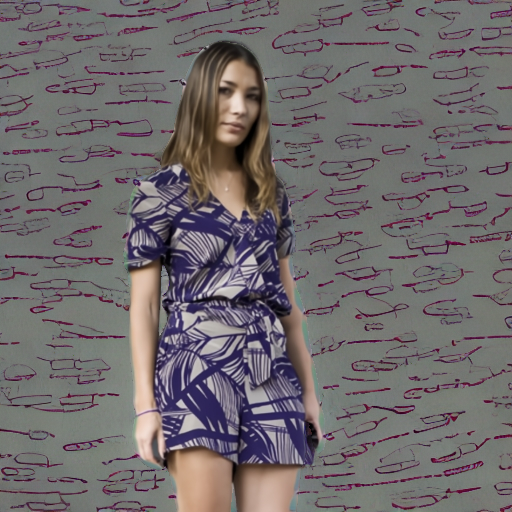





JPEG Compression
Prompt: "in a health and wellness center"
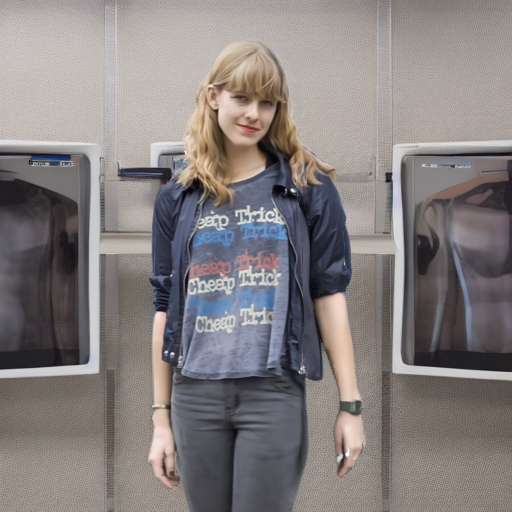



@inproceedings{ozden2026diffvax,
title={DiffVax: Optimization-Free Image Immunization Against Diffusion-Based Editing},
author={Ozden, Tarik Can and Kara, Ozgur and Akcin, Oguzhan and Zaman, Kerem and Srivastava, Shashank and Chinchali, Sandeep P and Rehg, James M},
booktitle={The Fourteenth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2026},
}